- HOME >
- Research activities
Ibaraki Cohort study: Scientific evidence-based transdisciplinary research for childcare support
R-GIRO research program Archive
 Recently, the childcare environment has changed greatly owing to the decline in birthrate, aging population, and increased participation of women in society and nuclear families. The stress and burden of childcare, especially for mothers, are important issues. Additionally, anxiety about pregnancy and delivery tends to be higher in late childbirths. Given the changes that occur in children’s environments, the development of children's social skills, such as self-control and cooperation, is also considered an issue that requires more attention. In childcare and education, there is growing interest in understanding and providing specific support to children.
Recently, the childcare environment has changed greatly owing to the decline in birthrate, aging population, and increased participation of women in society and nuclear families. The stress and burden of childcare, especially for mothers, are important issues. Additionally, anxiety about pregnancy and delivery tends to be higher in late childbirths. Given the changes that occur in children’s environments, the development of children's social skills, such as self-control and cooperation, is also considered an issue that requires more attention. In childcare and education, there is growing interest in understanding and providing specific support to children.
This project involves a longitudinal study aimed at clarifying the influence of social and physical environmental factors on parenting and children’s development from multiple perspectives. Through successive investigations with children (ranging from infants to preschoolers) and their parents, we aimed to develop and implement a childcare support system that can promote early detection and intervention for problems in parent-child interaction.
The project has remarkable academic significance as it involves transdisciplinary developmental research with quantitative and qualitative longitudinal data using multiple methods, such as behavioral measurement devices (digital pen, motion capture, DeepLabCut, etc.), behavioral observations (using the Interaction Rating Scale), measurements of physiological indicators (oxytocin, cortisol), interviews, and questionnaires.
 China, Japan, and Korea, which are part of the East Asian cultural sphere, have much in common in terms of geography, history, and culture. This project forms a collaborative system with researchers and experts from the three countries to examine and solve common social problems, aiming to compare the similarities and differences among the three neighboring countries from an international perspective and to provide useful information and effective solutions for each other.
China, Japan, and Korea, which are part of the East Asian cultural sphere, have much in common in terms of geography, history, and culture. This project forms a collaborative system with researchers and experts from the three countries to examine and solve common social problems, aiming to compare the similarities and differences among the three neighboring countries from an international perspective and to provide useful information and effective solutions for each other.
Furthermore, with the cooperation of Indonesian researchers, we conduct a survey of the situation of families in the Islamic world using a trilateral survey scheme. This research project attempts to conduct sufficient field research and establish more local (indigenous) frameworks.
Survey on the actual conditions and needs of child-rearing households related to the new coronavirus infection (COVID-19) and enhancement of support
 The recent COVID-19 pandemic has had a major impact on households that raise children. In addition to the stress caused by the refrain from going out, closure of schools, telecommuting, and anxiety about infection, the increased time spent with family members has led to concerns about the risk of domestic violence (DV) and child abuse by spouses. Moreover, as husbands and children work remotely, the burden on wives increases, and problems arise where wives are unable to play an active role in society. In response to these situations, our laboratory aims to provide necessary evidence-based support at the time by conducting continual surveys of the actual conditions and needs of child-rearing households in cooperation with government agencies. We also conducted international comparative research based on socio-cultural factors (policies, public health, views on child-rearing, etc.) in East Asian countries.
The recent COVID-19 pandemic has had a major impact on households that raise children. In addition to the stress caused by the refrain from going out, closure of schools, telecommuting, and anxiety about infection, the increased time spent with family members has led to concerns about the risk of domestic violence (DV) and child abuse by spouses. Moreover, as husbands and children work remotely, the burden on wives increases, and problems arise where wives are unable to play an active role in society. In response to these situations, our laboratory aims to provide necessary evidence-based support at the time by conducting continual surveys of the actual conditions and needs of child-rearing households in cooperation with government agencies. We also conducted international comparative research based on socio-cultural factors (policies, public health, views on child-rearing, etc.) in East Asian countries.
Studies on children's writing and drawing using a behavioral measurement device ‘digital pen’
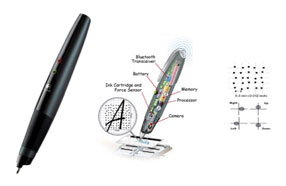 Collaborating with researchers at Seldage in France, we are conducting research on children's writing and drawing activities using a behavioral measurement device called the "digital pen" (ANOTO DP201). The digital pen accurately measures and records the drawing process, such as the speed at which the child draws the picture, pressures, drawing orders, and stroke information of the trajectory, and can also play back the trajectory repeatedly.
Collaborating with researchers at Seldage in France, we are conducting research on children's writing and drawing activities using a behavioral measurement device called the "digital pen" (ANOTO DP201). The digital pen accurately measures and records the drawing process, such as the speed at which the child draws the picture, pressures, drawing orders, and stroke information of the trajectory, and can also play back the trajectory repeatedly.
In addition to investigating the control of strokes, the ability to structure stroke units, and the developmental process of these skills, we also applied the system to drawing tests, such as Ray's Complex Figures, the Bender-Gestalt Test, and the Draw-A-Person Test.
Measurement and development of visual attention using the d2-R test, and the cross-national comparative study
The d2-R test, originally developed in the 1960s as the “d2 test” to evaluate driver proficiency in Germany, now plays a prominent role in measuring people’s visual attention not only in research but also in practice. One benefit of this test is its simple procedure, which requires only five minutes. The test is widely used to measure attention deficits in children, obsessive–compulsive disorder in adults, attention disorder in elderly people, and cerebral damage in the clinical setting (Brickenkamp & Zillmer, 1998). In order to standardize this test in Japan, we investigated the relationship between developmental changes and ADHD tendencies, as well as comparisons with data from France and Germany, with the cooperation of about 600 participants ranging in age from 6 to 80 years.
Click here to download the Japanese version of the d2-R test form.
d2.pdf






